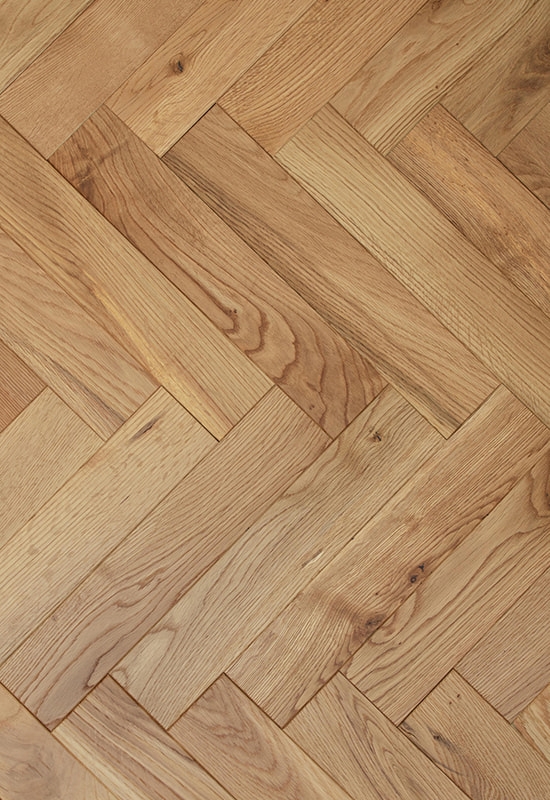
When it comes to engineered wood flooring, the choice of core material plays a pivotal role in determining the product’s overall performance, cost-efficiency, and application range. Two of the most widely used core options are high-density fiberboard (HDF) and plywood. While both cores serve as structural backbones beneath a real wood veneer, their differences in composition and behavior under various conditions can significantly affect end results. As a manufacturer and exporter specializing in HDF-engineered wood flooring, we frequently guide our clients through this technical comparison to help them make informed decisions based on their project requirements.
HDF, made by compressing wood fibers with resin under high pressure, results in an exceptionally dense and uniform material. This density ensures tight locking systems for click-installation flooring and minimizes the risk of delamination. Plywood, on the other hand, consists of multiple layers of wood veneer bonded together, offering natural resistance to moisture due to its cross-grain structure. However, it can also have variability in quality depending on the wood species and glue used in manufacturing, making performance somewhat inconsistent across sources and suppliers.
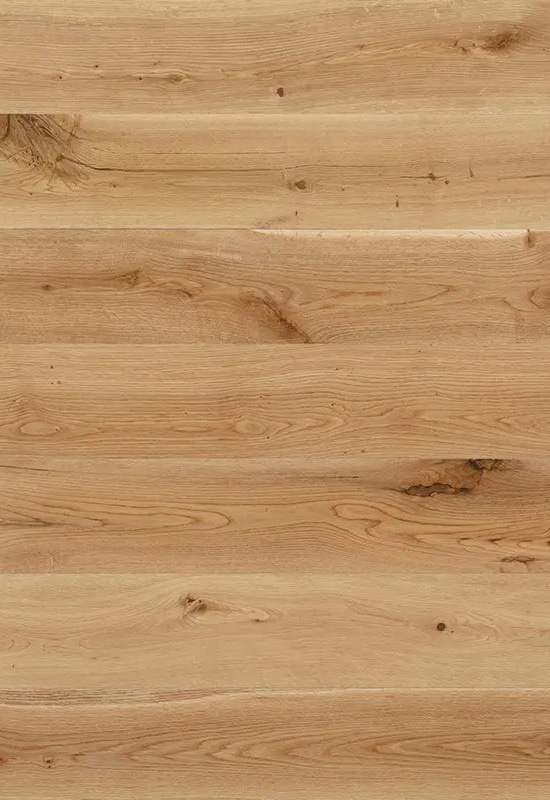

From a dimensional stability standpoint, HDF core flooring is less prone to expansion and contraction under fluctuating indoor climates. This trait makes HDF-engineered wood flooring especially well-suited for temperate and controlled environments such as modern apartments, office spaces, and large-scale residential projects. Plywood cores can sometimes outperform HDF in more extreme or moisture-variable conditions, such as over unconditioned concrete subfloors or in coastal climates, but usually at a higher cost and with stricter installation requirements.
One of the key advantages of HDF-core flooring lies in its precision milling. The compactness of HDF allows for highly accurate machining, which supports seamless installation and reduces the likelihood of joint gaps or movement over time. This level of consistency is harder to achieve with plywood cores, which may vary in density and flatness depending on their construction. For customers looking for a reliable, budget-conscious option without sacrificing aesthetics, HDF-engineered wood flooring offers a competitive balance between quality and value.
From a cost-efficiency perspective, HDF also tends to be more affordable to produce and ship due to its consistent density and optimized panel dimensions. That translates into lower prices for project managers, wholesalers, and retailers—without compromising surface finish or design versatility. In fact, the stability of the HDF core often enables the use of thinner veneers without performance loss, further driving material savings and sustainable production practices.
Of course, it's not a one-size-fits-all scenario. When discussing supply options with B2B clients, we often assess the core selection based on end-use environments, regulatory requirements, and customer priorities—be it budget, moisture resistance, or structural performance. Our role as a professional HDF-engineered flooring supplier is not just to deliver a product but to match the right construction to the right application with precision.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Français
Français












 +86-572-2118015
+86-572-2118015 No.598. Gaoxin Road, Huanzhu Industrial Zone, Huzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China, 313000
No.598. Gaoxin Road, Huanzhu Industrial Zone, Huzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China, 313000 