When it comes to choosing flooring that balances visual appeal, stability, and value, the internal composition matters more than most buyers realize. HDF-engineered wood flooring isn’t just about a hardwood surface—it’s a well-thought-out multi-layer system designed to deliver consistent performance in real-world conditions. Understanding what each layer does and how it contributes to the floor’s overall behavior is key to making an informed purchase, especially for environments that demand both aesthetics and reliability.
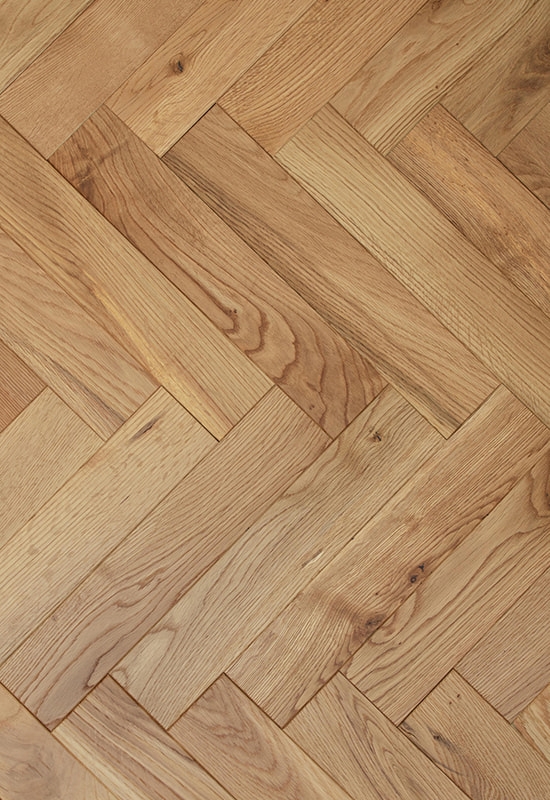
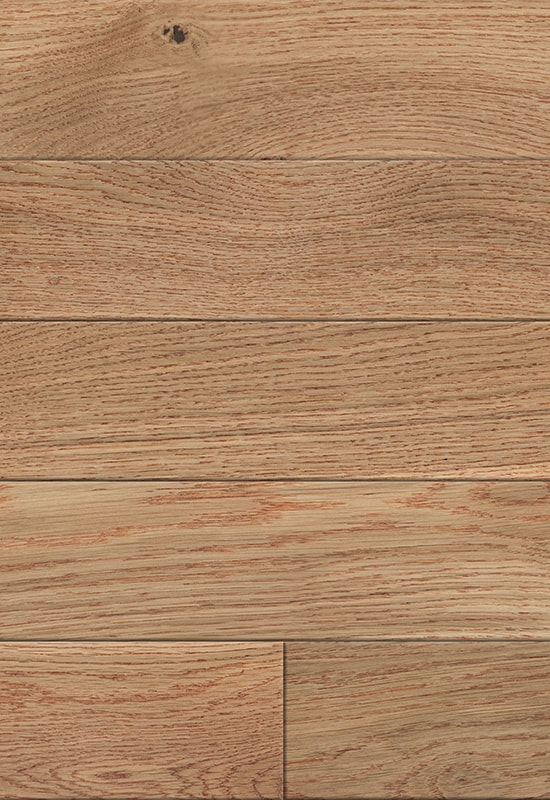
At the top of this structure is the hardwood veneer layer, which is what gives HDF-engineered flooring its natural wood appearance. This layer is made of real timber, carefully selected and processed to retain the grain, color variation, and texture of solid hardwood. While it’s thinner than a solid plank, modern slicing and finishing techniques ensure that it looks indistinguishable from traditional wood once installed. The thickness of this veneer can vary by product tier, but it’s always bonded firmly to the core to ensure both visual consistency and structural cohesion.
Beneath that lies the high-density fiberboard core, which is what really defines HDF-engineered wood flooring. HDF is made by compressing wood fibers with resin under high pressure, resulting in a board that is denser and more dimensionally stable than plywood or softwood cores. This density is crucial in environments where temperature and humidity shifts occur regularly, like in air-conditioned homes or commercial interiors. The core resists expansion and contraction, helping the floor maintain its shape over time and reducing the risk of warping, cupping, or gapping.
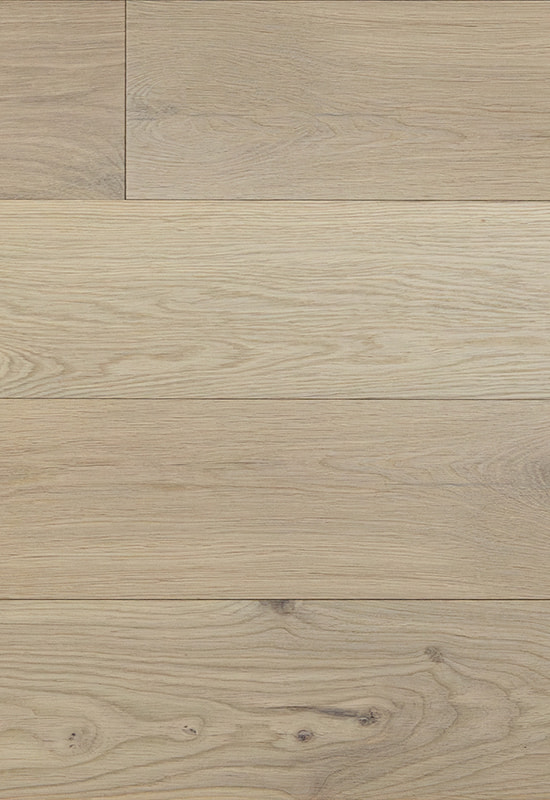

Another hidden but critical component is the balancing or backing layer, typically made of resin-impregnated paper or a stabilizing veneer. This layer plays a counterbalancing role, ensuring that the floorboard remains flat and resists curling after installation. When this backing is engineered correctly and matched to the properties of the top layer and core, it helps the entire structure perform more predictably under stress. This is one of the reasons why HDF flooring maintains its integrity better than many alternatives in its category.
The adhesives used to bind these layers together also play an essential role in performance and durability. Manufacturers of high-quality HDF-engineered wood flooring typically use eco-certified adhesives that comply with international standards for formaldehyde emissions and structural bonding. The quality of this glue line affects not only the longevity of the floor but also its resistance to delamination under moisture exposure or temperature swings. That’s why investing in a product with verified bonding technology can significantly extend the lifespan of your floor.
From a manufacturing perspective, each layer must be precisely calibrated to match the others in moisture content, dimensional tolerances, and elasticity. A well-balanced engineered plank is not simply a sum of parts—it’s the result of controlled processes, advanced material science, and real-world testing. As a manufacturer with industry experience, we know that even small deviations in layer thickness or core density can lead to performance issues down the line. That’s why attention to these details is part of what separates premium HDF flooring products from the rest.
Ultimately, the strength of HDF-engineered flooring lies not only in its materials but in the way those materials are combined. When done right, the multi-layer construction offers a reliable, visually appealing solution that adapts well to modern interior spaces. For homeowners, designers, and developers looking for long-term value, this flooring technology delivers a smart balance of beauty and durability that’s hard to beat.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Français
Français
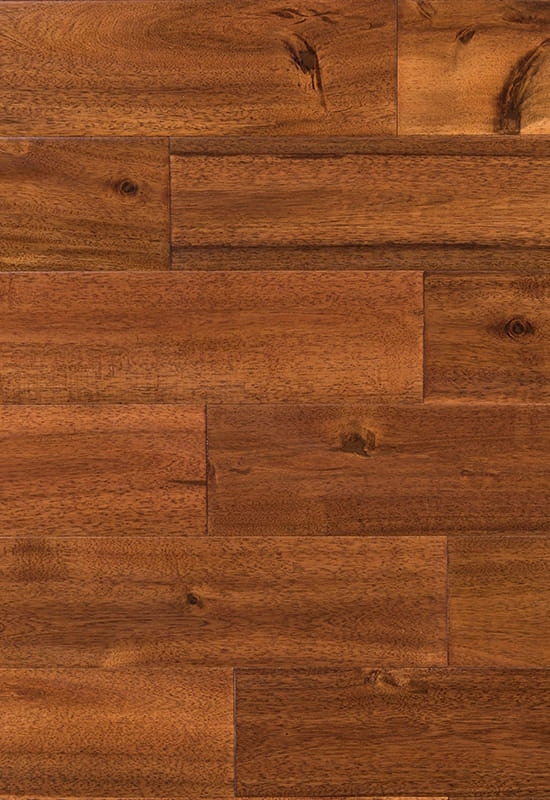
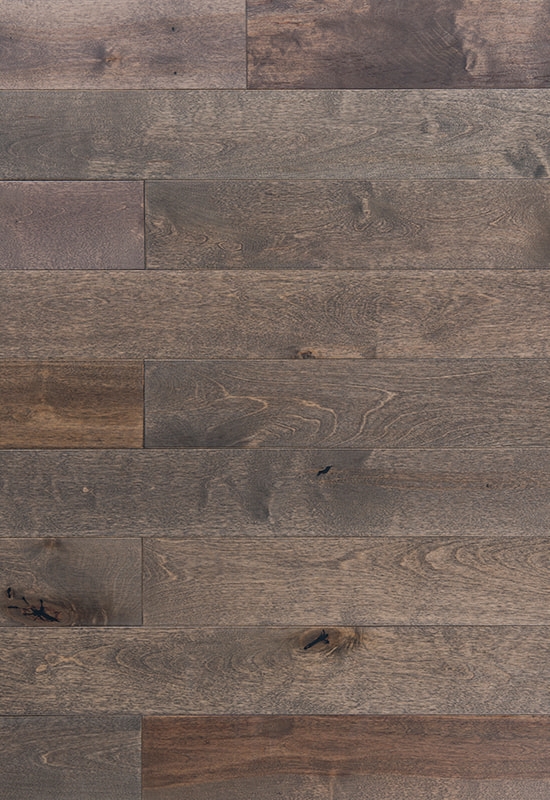
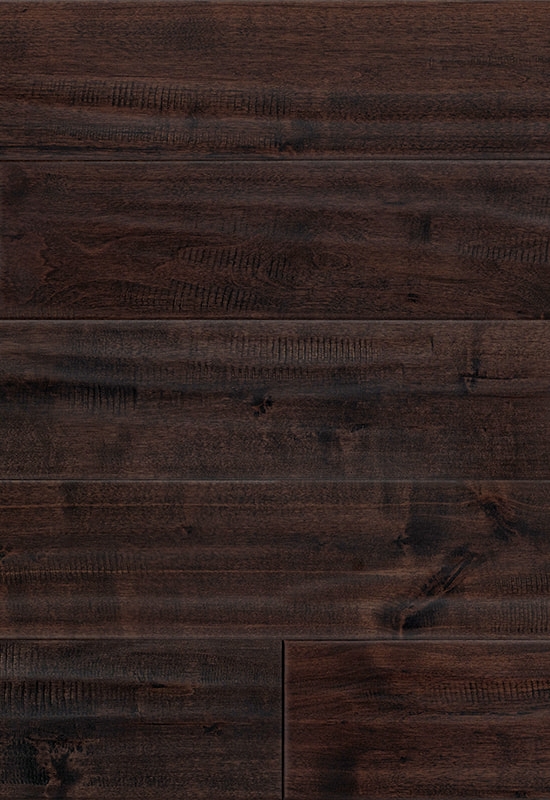
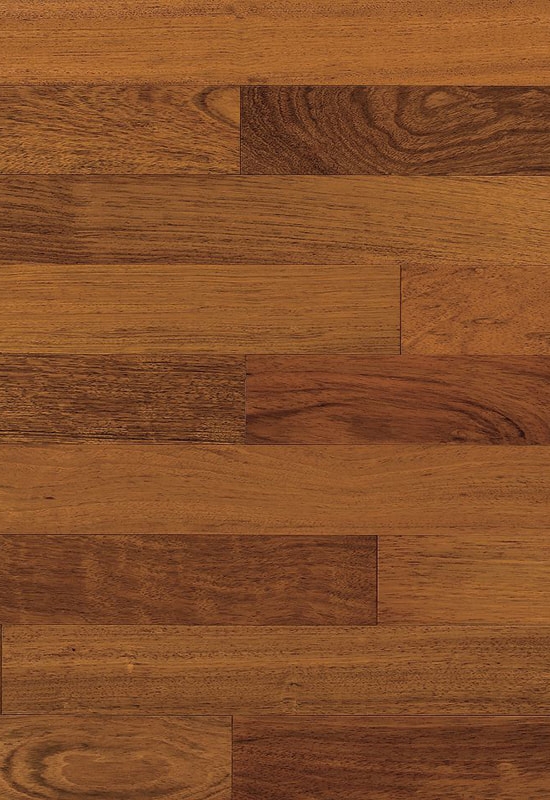












 +86-572-2118015
+86-572-2118015 No.598. Gaoxin Road, Huanzhu Industrial Zone, Huzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China, 313000
No.598. Gaoxin Road, Huanzhu Industrial Zone, Huzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China, 313000 