1. Understanding Laminate and Engineered Flooring
Laminate and engineered flooring are two popular choices for modern homes, each offering distinct features. Laminate flooring is made by fusing multiple layers of synthetic material with a photographic wood layer on top. Engineered flooring, however, combines a real wood veneer over a plywood or high-density fiberboard core, providing the look and feel of natural hardwood.
2. Durability and Lifespan
Durability is a key factor in choosing between laminate and engineered flooring. Laminate is highly resistant to scratches, dents, and moisture due to its wear layer, making it suitable for high-traffic areas. Engineered flooring, while slightly more sensitive to scratches, offers the authenticity and repairability of real wood, with sanding and refinishing possible depending on the veneer thickness.
3. Installation Methods
Installation differs between laminate and engineered flooring, affecting both cost and effort. Laminate usually features a click-lock system that allows floating installation without glue or nails, making it ideal for DIY projects. Engineered flooring can be installed via floating, gluing, or nailing, offering more flexibility but often requiring professional installation for the best results.
4. Maintenance and Cleaning
Both flooring types are relatively low maintenance, but there are differences to consider. Laminate is easy to clean with a dry or slightly damp mop, but excessive water can cause swelling. Engineered wood can tolerate more moisture than solid hardwood but should be cleaned with wood-friendly products to protect the veneer. Both floors benefit from using furniture pads to prevent scratches.
5. Cost Comparison
Cost is often a deciding factor for homeowners. Laminate flooring tends to be more budget-friendly, with lower material and installation costs. Engineered flooring, while more expensive, adds long-term value by offering the authentic appearance of hardwood and potential for refinishing. The choice often balances budget, desired aesthetics, and longevity.
6. Aesthetic Options
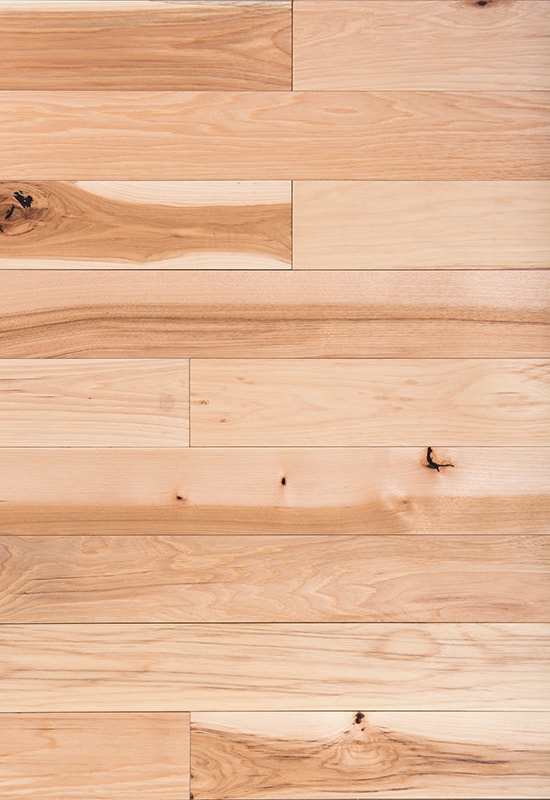
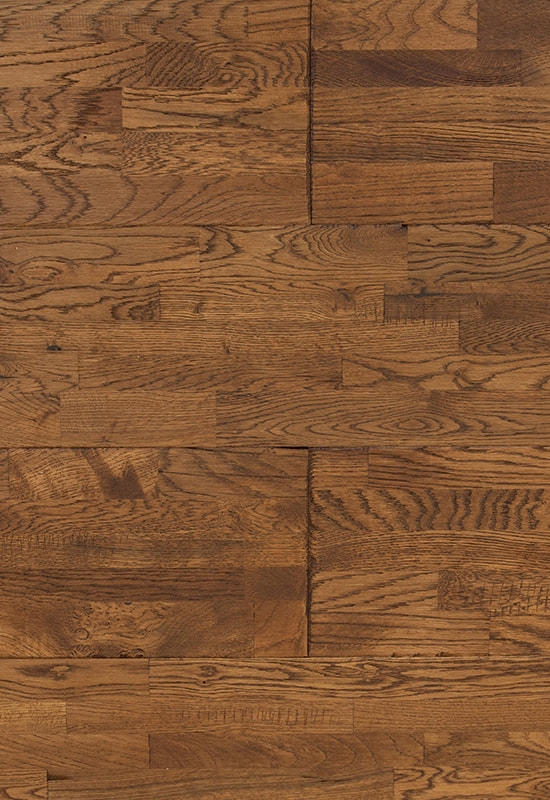
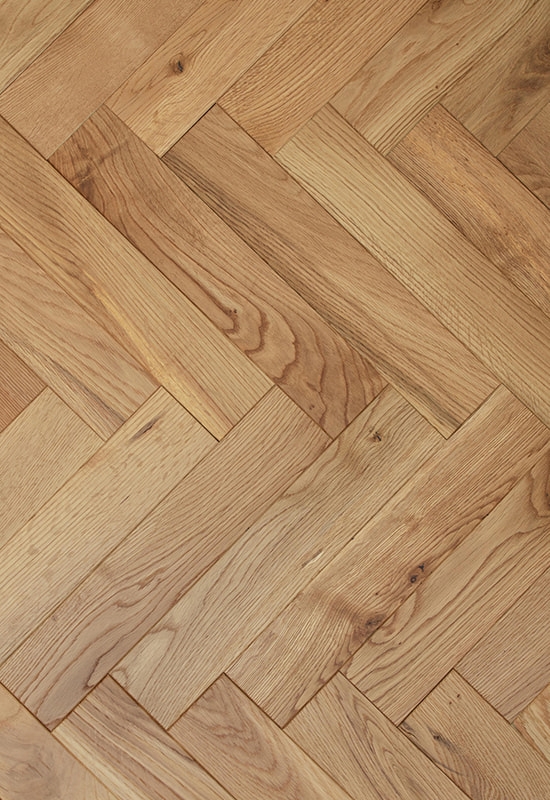
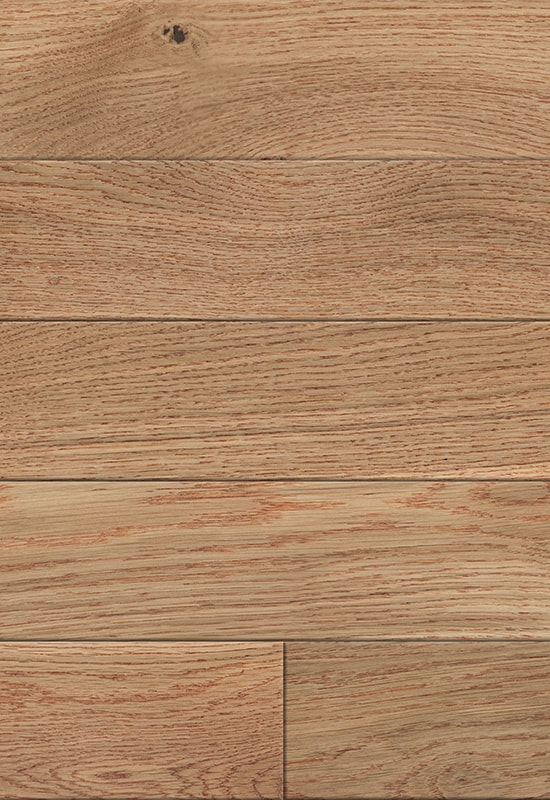
Aesthetic versatility is another important consideration. Laminate offers a wide range of designs and patterns, from traditional wood grains to modern textures, often mimicking exotic hardwoods. Engineered flooring features real wood veneers, delivering natural color variation, texture, and warmth that laminate cannot fully replicate.
7. Comparative Table: Laminate vs Engineered Flooring
| Feature | Laminate | Engineered Flooring |
| Material | Synthetic core with photographic wood layer | Real wood veneer over plywood or fiberboard |
| Durability | High resistance to scratches and dents | Moderate; can be refinished depending on veneer thickness |
| Installation | Click-lock floating system | Floating, glue-down, or nail-down |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean; avoid excess water | Requires wood-friendly products; can tolerate moderate moisture |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Appearance | Variety of printed designs; mimics wood | Authentic wood texture and natural variation |
8. Choosing the Right Flooring for Your Home
Choosing between laminate and engineered flooring depends on lifestyle, budget, and design goals. Laminate is ideal for families with children or pets, or for DIY installations where cost efficiency is important. Engineered flooring is perfect for homeowners seeking natural wood aesthetics, longer-term value, and the option to refinish the surface. Evaluating traffic levels, moisture exposure, and personal preferences will ensure the best choice for your space.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Français
Français












 +86-572-2118015
+86-572-2118015 No.598. Gaoxin Road, Huanzhu Industrial Zone, Huzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China, 313000
No.598. Gaoxin Road, Huanzhu Industrial Zone, Huzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China, 313000 